Al momento, questa pagina non è disponibile nella lingua scelta. È possibile visualizzare una traduzione automatica realizzata con Google Translate. Renishaw declina qualsiasi responsabilità relativa alla fornitura di tale servizio e specifica di non avere controllato la traduzione.
È possibile contattarci per richiedere ulteriore assistenza.
Additive manufacturing for medical and healthcare
Latest additive manufacturing case studies.
Case studies
Renishaw goes big on nanofiber
To help with ongoing personal protective equipment (PPE) shortages, Ontario-based nanofiber manufacturer, BIG-nano, has collaborated with Renishaw to create a local supply chain for protective masks using additive manufacturing (AM).
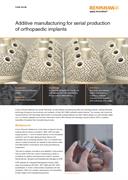
Additive manufacturing for serial production of orthopaedic implants
Croom Precision Medical has chosen Renishaw as their additive manufacturing (AM) and metrology partner, utilising Renishaw technology throughout the production and validation of their ISO13485 certified medical devices. The company has found that using Renishaw's AM technology allows them to incorporate complex features into their implant design at a commercially viable cost.
Streamlining additive manufacturing for spinal implants
Global engineering company, Renishaw, collaborated with two innovative technology companies to demonstrate the capability of metal additive manufacturing (AM) technology to produce lightweight spinal implants that mimic the mechanical properties of bone. As part of the project, Irish Manufacturing Research (IMR) designed and manufactured a series of representative spinal implants. IMR designed the implants using software from nTopology and produced them on a Renishaw RenAM 500M metal AM system.
A swift transition to digital dentistry
A partnership with Renishaw saw the introduction of additive manufacturing to Swift, fitting seamlessly into a newly implemented digital workflow. Renishaw supplied an AM250 system, which uses a high-powered ytterbium fibre laser to fuse fine metallic powders together to create a final three-dimensional structure.
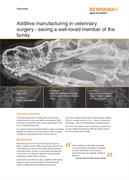
AM in veterinary surgery – saving a well-loved member of the family
A seven-year-old Bernese Mountain Dog with a tumour on the left side of his maxilla (upper jaw) had few options other than total excision of the growth followed by reconstruction. A customised 3D printed titanium implant supporting the dog's bone structure was the most appropriate treatment due to the complexity of the region, requiring significant design and manufacturing freedom.
Proslab ensures absolute accuracy with AM
Proslab turned to global engineering company Renishaw to fully digitalise its manufacturing process using additive manufacturing.Before working with Renishaw, Proslab introduced a partially digital workflow, using 3D scanning and design tools to design dentures.
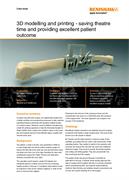
3D modelling and printing
Complex reconstructive surgery can significantly benefit from a digital workflow and pre-planning processes to help optimise operating theatre productivity with excellent surgical results. Read how Renishaw used its additive manufacturing (metal 3D printing) expertise to help the University Hospital of Wales (UHW) treat a patient who suffered cancer of the lower jaw and required removal of the affected region coupled with reconstructive work.
Mission to Nepal
Metal 3D printing's real life applications are ever increasing. Read how a NRIEF's mission to Nepal has taken advantage of this technology by helping a young mother who was a road traffic collision victim.
Digital evolution of cranial surgery
From complex reconstructive facial surgery to orthopaedic and trauma surgery, advances in additive manufacturing have inspired a growing number of progressive surgeons to commission metal 3D printed patient specific implants (PSIs) and cutting guides for both complex and straightforward procedures.
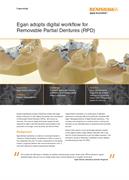
Egan adopts digital workflow for Removable Partial Dentures (RPD)
Global engineering company Renishaw worked with Egan Dental Laboratory to fully digitise the design and manufactureof Removable Partial Dentures (RPDs), also known as chromes. The move to digital techniques halved the time required to make a chrome framework and resulted in the production of stronger, more accurate, yet thinner RPDs.