Study catalysis with Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is increasingly being used in the study of catalysts and catalytic reactions. This provides critical information on the mechanisms, helping to improve conversion efficiency.
Analyse a wide range of catalytic systems
Raman spectroscopy is particularly powerful for these studies:
- discriminate between multiple catalyst phases
- investigate reaction mechanisms
- conduct in situ measurements
- in reactive environments
- at high temperatures and pressures
- in aqueous solutions
- reveal by-products and other unknowns
Versatile access to reaction vessels
When it is not possible for you to get the sample close to the instrument, Renishaw's systems can acquire Raman data by using fibre optic probes or directly coupled optics. These are available with sample viewing capabilities, so you can see the position of the laser spot and ensure it is in the correct analysis location.
Environmental control
Most catalysts are fundamentally unstable in air. Renishaw can provide suitable cells which enable you to keep your samples in the right environment. You can control temperature, humidity, and gaseous environment when performing in situ analysis.
Control the power
Some catalysts are prone to laser damage. We make it easy to select the most appropriate laser power for analysis. Renishaw also uses a line focus capability which lowers the power density of the light and reduces the risk of sample modification. You can maximise the Raman signal without having to risk laser damage, and can be confident the data accurately represent your material.
We're here when you need us
To find out more about this application area, or an application that isn't covered here, contact our applications team.
Contact our applications team
Related stories
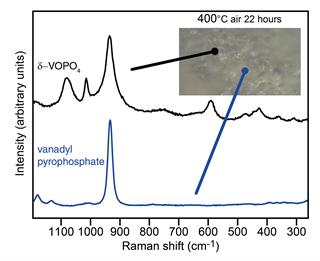
'Raman-spectrokinetics' for improved solid catalysts
The Carrero group, based at Auburn University, undertakes fundamental studies to improve and develop more efficient and sustainable catalytic processes. They aim to develop the best catalysts using in situ / operando Raman spectroscopy to gather molecular, structural, and mechanistic insights.