Denna sida finns för närvarande inte på ditt språk. Du kan
översätta
den automatiskt
med Google Translate. Vi ansvarar inte för att tillhandahålla denna tjänst och
vi har inte kontrollerat översättningsresultaten.
Kontakta oss om du behöver ytterligare hjälp.
Analyse biological tissues with Raman spectroscopy
A non-invasive and label-free technique, Raman spectroscopy is an ideal analytical tool for tissue analysis.
You can extract a full spectrum of chemical information (from entities such as nucleic acids, proteins and lipids) without the need for targeting biomolecules, markers, stains or dyes. Unlike many other analysis techniques—such as western blot, GC/MS, and MALDI-TOF—Raman analysis does not require the sample to be homogenized.
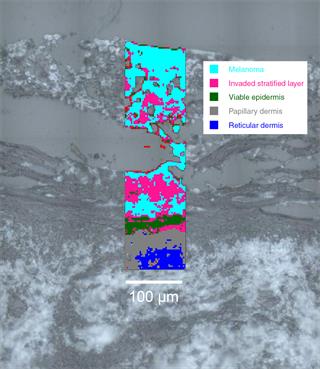
Quickly and accurately identify tissue layers
Distinguish, identify and demarcate pre-cancerous, cancerous and healthy tissues.
- No need for conjugation with antibodies: save both money and time when optimising protocols
- Reliably demarcate and objectively identify anatomical layers in the tissues, based on their total molecular composition. Delineate tumour margins
- Avoid subjective colourimetry and morphology-based analysis
- Identify chemical changes in the tissues that have not manifested themselves in morphological changes (e.g. levels of DNA/RNA, glycogen, lipid, protein, lipid phase and DNA integrity)
Understand biological systems
Get a complete chemical analysis of tissues and understand the underlying mechanism of their changes.
Study:
- the development of an organism
- the pathogenesis of diseases
- tissue's response to drugs or stimulants (e.g. chemotherapeutic agents, toxins and anti-inflammatories)
Examine in one procedure:
- changes in the level and conformation of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids and carbohydrates
- the presence of mineral deposits (e.g. calcification in breast tissue and atherosclerosis)
- the redox states of heme proteins (e.g. neuroglobins and myoglobins)
Image tissues
Renishaw's StreamLine™ technology is particularly suited to generating tissue images. Its line-focus geometry enables you to use high laser powers whilst avoiding photothermal damage to the tissue. This maximises signal levels and gives you images in the shortest possible time.
Study uneven surfaces
With StreamLine's Surface capability, you can generate images of samples, even if they are not flat.
Slide scanning automation
You can configure Renishaw's fully automated Raman systems to scan sequentially multiple histological sections and run unattended. This saves you time and enables you to maximise the productivity of your Raman system.
We're here when you need us
To find out more about this application area, or an application that isn't covered here, contact our applications team.
Contact our applications team
Webinar – Predicting disease in biofluids and tissues with Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy has become a key analysis technique within medicine. It can retrieve detailed chemical information from samples in their endogenous, unaltered form. This makes Raman an effective method for assessing disease state within biofluids and tissues.
In this webinar we will show how Renishaws compact and easy-to-use RA816 biological analyser can help bring Raman spectroscopy to the clinic. It can rapidly collect large numbers of spectra from ex vivo samples. This enables you to develop models for predicting and detecting disease in biofluids and tissues.
Watch the webinar
You may be interested in these papers:
Kast et al (2014) J Neurooncol doi 10.1007/s11060-014-1536-9
Bonifacio et al (2010) Analyst 135: 3193-3204
Related stories
Raman spectroscopys potential to identify diseased cartilage in osteoarthritis
A group of researchers and clinicians at University College London, Royal Veterinary College and Charing Cross Hospital, led by Dr Riana Gaifulina, have demonstrated that Raman spectroscopy could determine the grade of cartilage erosion and overall osteoarthritis disease state. This could lead to an earlier identification and treatment of osteoarthritic degeneration.
Raman spectroscopy of biological tissue for rapid classification of brain gliomas
Researchers used Renishaw RA816 Biological Analyser to identify the genetically different subtypes of brain gliomas in a surgical setting.
Raman spectroscopy used to detect radiation damage in cells and tissues during cancer treatment
A multidisciplinary group of scientists and engineers are using Raman spectroscopy to understand the damage in cells and tissues caused by radiation used in cancer treatment.
Raman spectroscopy used to study diseases at the Children's Hospital of Michigan
The Children's Hospital of Michigan and Wayne State University use a Renishaw inVia confocal Raman microscope in the study of childhood diseases.