Denna sida finns för närvarande inte på ditt språk. Du kan
översätta
den automatiskt
med Google Translate. Vi ansvarar inte för att tillhandahålla denna tjänst och
vi har inte kontrollerat översättningsresultaten.
Kontakta oss om du behöver ytterligare hjälp.
Identifying particulates and contaminants with Raman spectroscopy
Contaminant identification is one of the largest Raman application areas. Almost all manufacturing sites around the world are at threat from contamination, which can cause costly production stoppages. This also extends to environmental and regulatory monitoring of materials and pollutants.
Examples of contaminants include:
- particulates on semiconductor wafers
- corrosion products on metal items
- oils and cutting fluids on manufactured items
- foreign matter in pharmaceutical ingredients
- polymer particles (such as microbeads) within large water sites
Raman analysis of contaminants
Raman spectroscopy is a great technique to identify the contamination, and help determine its source. Renishaw Raman systems get you the best possible data, helping you identify contaminants rapidly and easily. They offer:
- high sensitivity, with sub-micrometre spatial resolution – analyse tiny traces of material and thin films
- Raman spectral databases – so you can quickly identify contaminants
- multiple lasers, from the UV to IR – have the flexibility to analyse a wide range of samples
- non-destructive and non-contacting analysis – preserve the evidence of contamination
- options for locating, analysing and automating measurements on particles of different sizes
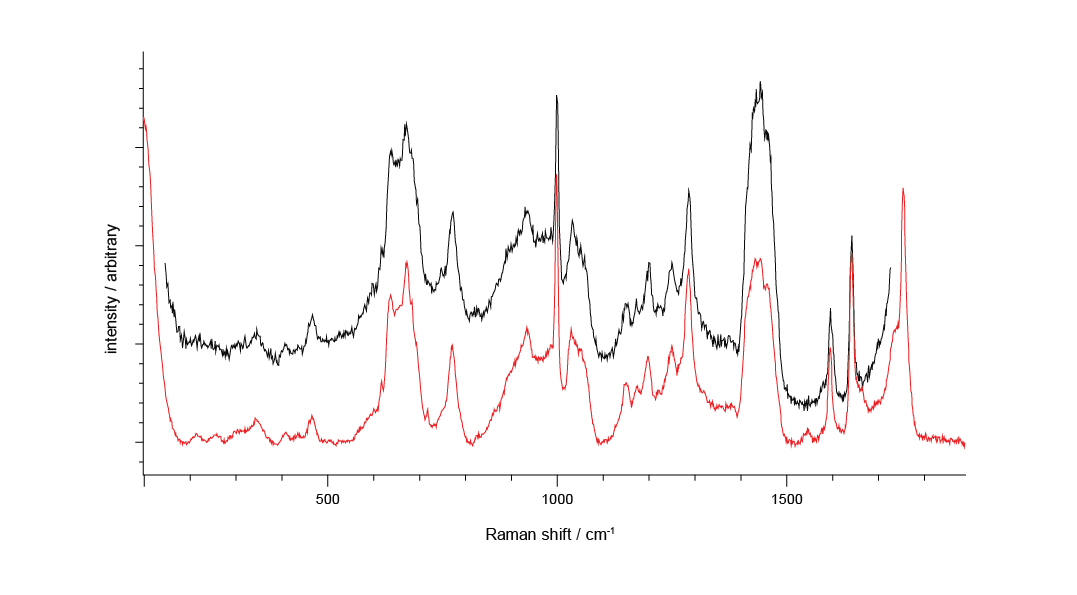
Raman spectrum of an unknown contaminant (black) with a library spectrum (red) of a UV adhesive. The clear match between the spectra enables identification of the unknown and highlights the strength of the inLux interface for contamination analysis. Data collected with 532 nm laser excitation.
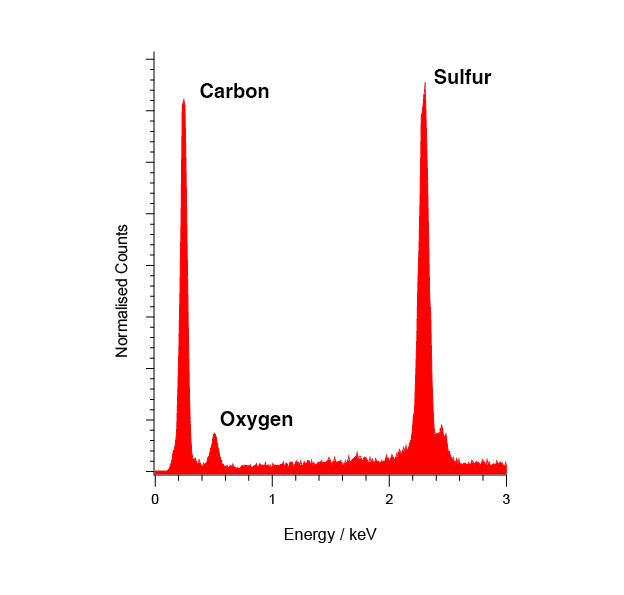
The EDS spectrum of the contaminant provides elemental information, but does not allow for full identification of the contamination.
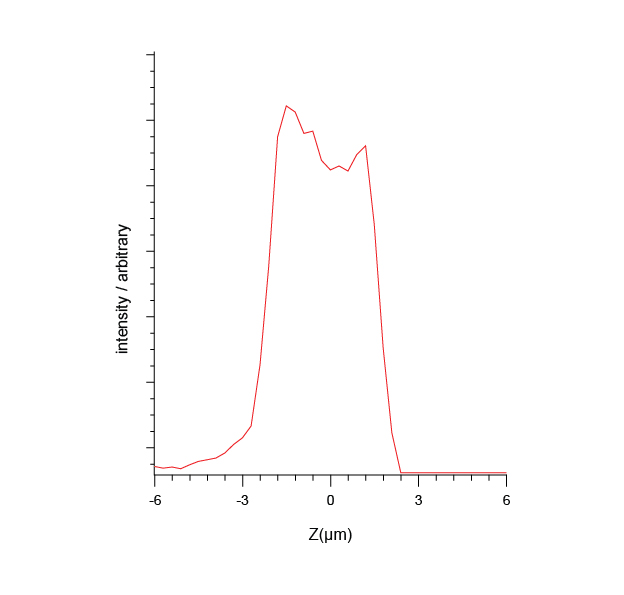 Raman confocal depth profile. The confocal analysis enables the contaminant thickness to be quantified.
Raman confocal depth profile. The confocal analysis enables the contaminant thickness to be quantified.Watch Raman Explored seminar presentations
Our recent seminar featured groundbreaking research including:
- Art authentication
- Cultural heritage and conservation
- Minerals, fossils and fossil forgeries
- The origin of the Altar Stone at Stonehenge
- Spectroscopy on Mars
Find out how Raman spectroscopy is making an impact in cultural heritage, conservation and geoscience!
We understand the problem
No matter how careful the manufacturing process, things change and contamination can occur.
Renishaw is at the forefront of advanced manufacturing and is renowned for the high quality of its products. Our engineers use inVia Reflex confocal Raman microscopes as part of Renishaw's quality control processes; we understand the challenges of contamination.
We're here when you need us
To find out more about this application area, or an application that isn't covered here, contact our applications team.
Contact our applications team
Related stories
Identifying microplastics in the environment
The Danish Technological Institute is using a Renishaw Raman spectroscopy system to characterise the extent of microplastic pollution entering Danish wastewater and rainwater systems.





